Last updated: April 25, 2024
How to activate data observability for Amazon Redshift
Read this guide to learn how to connect DQOps to AWS Redshift from the UI, command-line interface, or directly in YAML files, and activate monitoring.
Overview
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud from Amazon Web Services.
Redshift can handle analytic workloads on big data sets stored by a column-oriented DBMS principle
Prerequisite credentials
To add Redshift data source connection to DQOps you need a Redshift account.
Amazon Redshift uses an elastic IP address for the external IP address. An elastic IP address is a static IP address. In case of restrictions, you need to add the IP address used by DQOps to Allowed IP Addresses in Redshift Network Policies.
Add Redshift connection using the user interface
Navigate to the connection settings
To navigate to the Redshift connection settings:
-
Go to the Data Sources section and click the + Add connection button in the upper left corner.
-
Select Redshift database type.
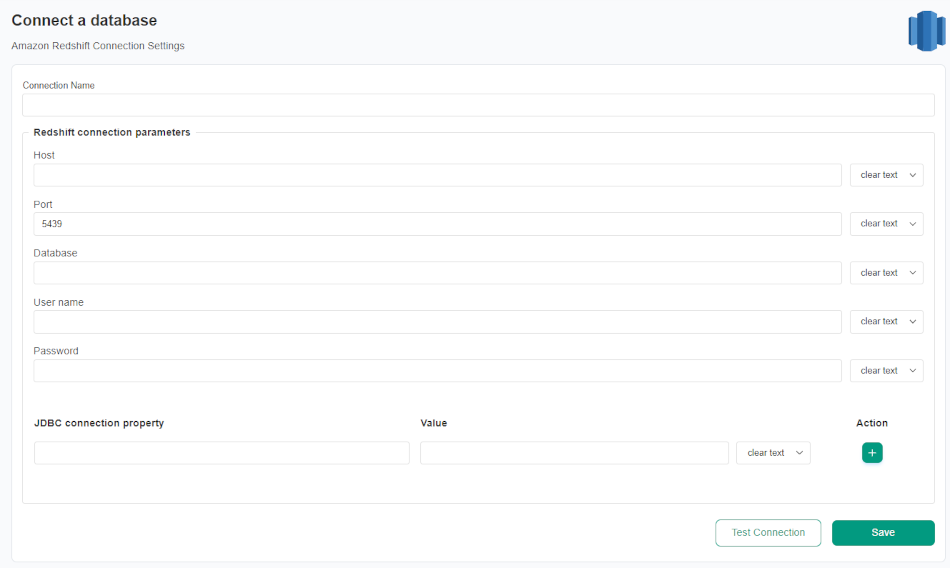
Fill in the connection settings
After navigating to the Redshift connection settings, you will need to fill in its details.
| Redshift connection settings | Property name in YAML configuration file | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection name | The name of the connection that will be created in DQOps. This will also be the name of the folder where the connection configuration files are stored. The name of the connection must be unique and consist of alphanumeric characters. | |
| Host | host |
Redshift host name. ClusterID and Region must be set in Host. Supports also a ${REDSHIFT_HOST} configuration with a custom environment variable. |
| Port | port |
Redshift port name. The default port is 5439. Supports also a ${REDSHIFT_PORT} configuration with a custom environment variable. |
| Database | database |
Redshift database name. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution. |
| Redshift authentication mode | redshift_authentication_mode |
The authentication mode for Redshift. Supports also a ${REDSHIFT_AUTHENTICATION_MODE} configuration with a custom environment variable. |
| User name | user |
Redshift user name. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution. |
| Password | password |
Redshift database password. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution. |
| Access Key ID | user |
Available when using AWS S3. Access Key ID for AWS authentication. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution. |
| Secret Access Key | password |
Available when using AWS S3. Secret Access Key for AWS authentication. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution. |
| JDBC connection property | Optional setting. DQOps supports using JDBC driver to access Redshift. See the Redshift documentation for JDBC connection parameter references. |
DQOps allows you to dynamically replace properties in connection settings with environment variables. To use it, simply change "clear text" to ${ENV_VAR} using the drop-down menu at the end of the variable entry field and type your variable.
For example:
To add optional JDBC connection properties, just type the JDBC connection property and the Value. The value can be in the ${ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE_NAME} format to use dynamic substitution.
For example:
To remove the property click on the trash icon at the end of the input field.
After filling in the connection settings, click the Test Connection button to test the connection.
Click the Save connection button when the test is successful otherwise, you can check the details of what went wrong.
Import metadata using the user interface
When you add a new connection, it will appear in the tree view on the left, and you will be redirected to the Import Metadata screen. Now we can import schemas and tables.
-
Import the selected data resources (source schemas and tables) by clicking on the Import Tables button next to the name of the source schema from which you want to import tables.
-
Select the tables you want to import or import all tables using the buttons in the upper right corner.
When new tables are imported, DQOps automatically activates profiling and monitoring checks, such as row count, table availability, and checks detecting schema changes. These checks are scheduled to run daily at 12:00 p.m. By clicking on the Advisor at the top of the page, you can quickly collect basic statistics, run profiling checks or modify the schedule for newly imported tables.
Add Redshift connection using DQOps Shell
To add a connection run the following command in DQOps Shell.
Fill in the data you will be asked for.
Connection name (--name): connection1
Database provider type (--provider):
[ 1] bigquery
[ 2] databricks
[ 3] mysql
[ 4] oracle
[ 5] postgresql
[ 6] duckdb
[ 7] presto
[ 8] redshift
[ 9] snowflake
[10] spark
[11] sqlserver
[12] trino
Please enter one of the [] values: 8
Redshift host (--redshift-host)[${REDSHIFT_HOST}]: localhost
Redshift port (--redshift-port) [${REDSHIFT_PORT}]: 5439
Redshift database (--redshift-database) [${REDSHIFT_DATABASE}]: testing
Redshift user name (--redshift-username) [${REDSHIFT_USER}]: testing
Redshift password (--redshift-password) [${REDSHIFT_PASSWORD}]: xxx
Connection connecton1 was successfully added.
Run 'table import -c=connection1' to import tables.
You can also run the command with parameters to add a connection in just a single step.
dqo> connection add --name=connection1
--provider=redshift
--redshift-host=localhost
--redshift-port=5439
--redshift-database=testing
--redshift-user=testing
--redshift-password=xxx
After adding connection run table import -c=connection1 to select schemas and import tables.
DQOps will ask you to select the schema from which the tables will be imported.
You can also add the schema and table name as a parameter to import tables in just a single step.
DQOps supports the use of the asterisk character * as a wildcard when selecting schemas and tables, which can substitute any number of characters. For example, use pub* to find all schema a name with a name starting with "pub". The * character can be used at the beginning, in the middle or at the end of the name.
Connections configuration files
Connection configurations are stored in the YAML files in the ./sources folder. The name of the connection is also
the name of the folder where the configuration file is stored.
Below is a sample YAML file showing an example configuration of the Redshift data source connection.
apiVersion: dqo/v1
kind: source
spec:
provider_type: redshift
redshift:
host: redshift-cluster-2.cds5vq1bzgx5.us-east-1.redshift.amazonaws.com
port: 5439
database: testing
user: testing
password: xxx
properties:
'connectTimeout': 15
incident_grouping:
grouping_level: table_dimension_category
minimum_severity: warning
max_incident_length_days: 60
mute_for_days: 60
Reference of all connection parameters
Complete documentation of all connection parameters used in the spec.redshift node is
described in the reference section of the RedshiftParametersSpec
YAML file format.
Configure the credentials
Using shared credentials
With DQOps, you can configure credentials to access AWS S3 directly in the platform.
Please note, that any credentials and secrets shared with the DQOps Cloud or DQOps SaaS instances are stored in the .credentials folder. This folder also contains the default credentials files pair for AWS named AWS_default_config and AWS_default_credentials.
If you wish to use AWS authentication, the content of the files must be replaced with your aws_access_key_id, aws_secret_access_key and region. You can find more details on how to manage access keys for IAM users in AWS documentation.
Warning
If you do not replace the content of the files, the default credentials will be loaded from system.
To set the credential file in DQOps, follow these steps:
- Open the Configuration section.
- Select Shared credentials from the tree view on the left.
- Click the edit link on the “AWS_default_credentials” file.
- In the text area, edit the aws_access_key_id and aws_secret_access_key, replacing the placeholder text.
-
Click the Save button, to save changes, go back to the main Shared credentials view.
-
Edit the region in AWS_default_config file and save the file.
Use the system default credentials after filling in the shared credential
If you still want to use default credentials from AWS, you must manually delete the .credentials/AWS_default_config and .credentials/AWS_default_credentials files from the DQOps credentials.
Next steps
- We have provided a variety of use cases that use openly available datasets from Google Cloud to help you in using DQOps effectively. You can find the full list of use cases here.
- DQOps allows you to keep track of the issues that arise during data quality monitoring and send alert notifications directly to Slack. Learn more about incidents and notifications.
- The data in the table often comes from different data sources and vendors or is loaded by different data pipelines. Learn how data grouping in DQOps can help you calculate separate data quality KPI scores for different groups of rows.